|
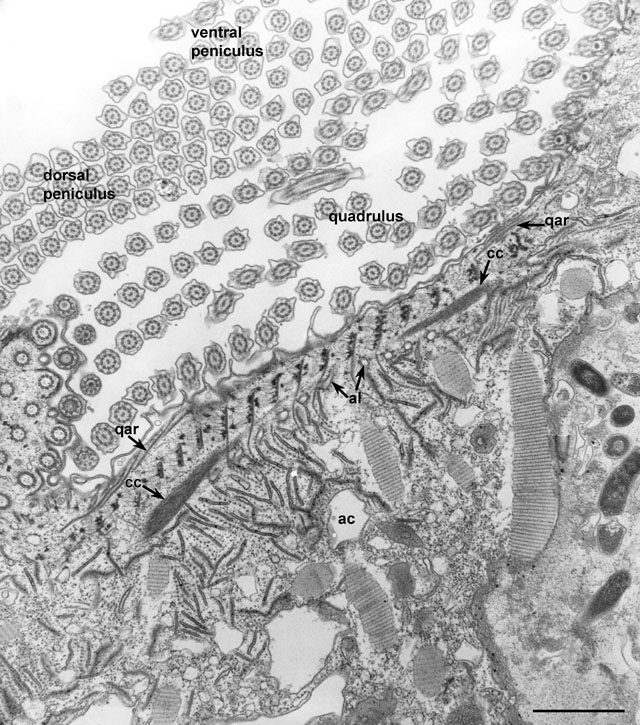
The left edge of the cytopharynx is bordered by a complex
architecture designed to transport a pool of flattened vesicles to
this edge where they will fuse with the cytopharyngeal membrane to
expand this membrane into a nascent phagosome. The buccal cavity
itself has the normal pellicle composed of the plasma membrane and
alveoli. Internal to this is a system of regularly shaped electron
opaque nodes that are bound together by whispy filaments to form a
reinforced border. This is part of the filamentous reticulum which is
found to a greater or lesser extent underlying the alveolar system of
the entire buccal cavity but not the cytopharynx itself. Arising from
the nodes are the cytopharyngeal microtubular ribbons that are spaced
at regular intervals. These ribbons, composed of about 12 microtubules
each, curve into the cytosol over a bundle of filaments called the
cytostomal cord (cc) which is an extension of the
centrin-containing infraciliary lattice. Numerous discoidal vesicles
are bound to one side of the microtubules. Associated with the
cytosomal cord are regularly spaced tubular extensions of the alveolar
sacs (al) that are connected by short fibers to the cord.
qar, accessory microtubular ribbons on the right edge of the
quadrulus; ac, acidosome. EM taken on 3/30/73 by R. Allen with
Hitachi HU11A TEM. Neg. 9,250X. Bar = 1µm. Published in part in J.
Cell Biol. 63:904-922, 1971.
|