|
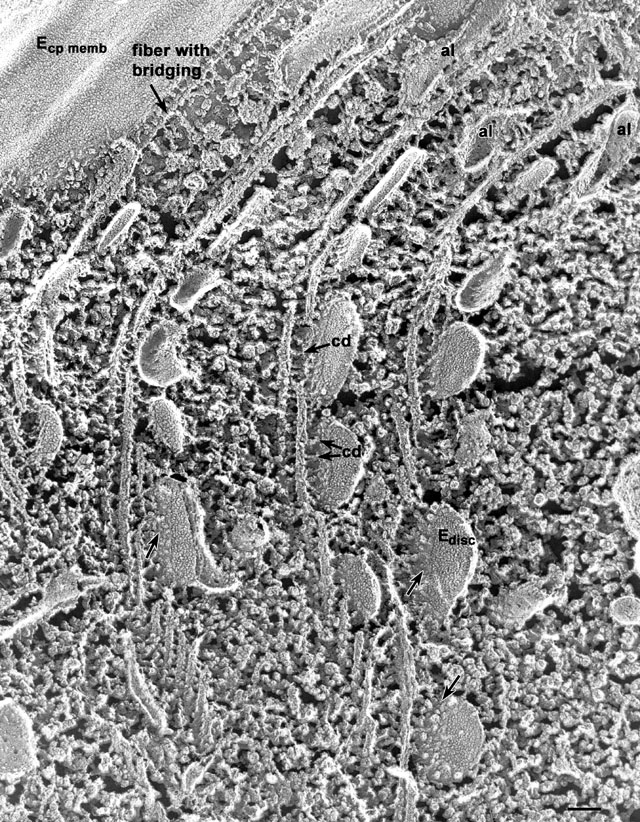
Quick-freeze deep-etch view of the discoidal vesicles that are linked
to the microtubular ribbons by bridges which are thought to be motor
proteins called cytoplasmic dynein (cd). We have isolated
cytoplasmic dynein (see Schroeder, Fok and Allen, J. Cell Biol.
111:2553-2562, 1990) and have shown that this motor can move
microtubules when a lawn of dynein molecules is tethered to a
coverslip. The microtubular ribbons are not linked to the membrane
directly but there is a fiber is linked to the membrane as well as to
the microtubule closest to the membrane (see Allen, J. Cell Biol.
63:904-922, 1974). Finally, the membranes of the discoidal vesicles
(disc) have been fractured to reveal their E faces which bear
many IMPs just like the E face of the cytopharynx membrane (top left).
The true cytosolic surface of the discoidal vesicles (arrows)
has many globular elements which are probably, in part, cytoplasmic
dynein complexes, whole or fractured off. al, alveolar fingers.
EM taken on 5/18/88 by C. Schroeder with Zeiss 10A TEM. Neg. 31,500X.
Bar = 0.1µm. Part published in Adv. Cell Mol. Biol. Memb. 28:311-337,
1993.
|