|
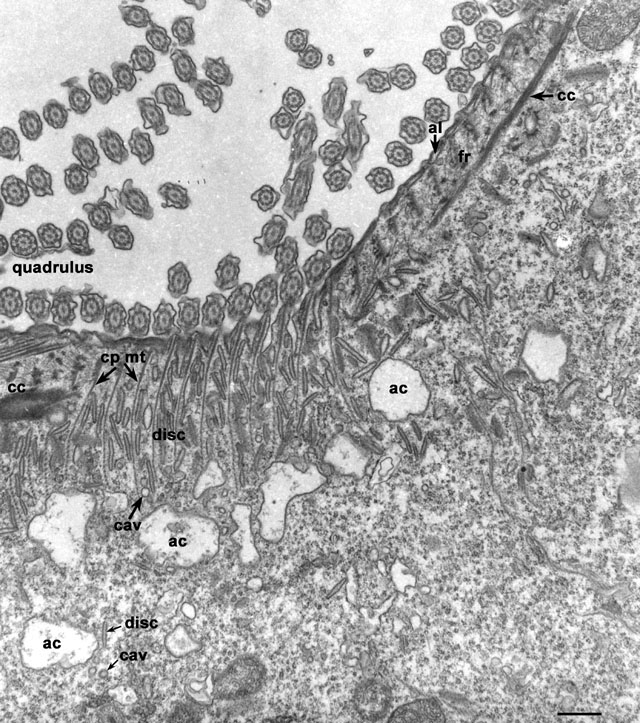
Structures at the left edge of the cytopharynx arise in contact with
the filamentous reticulum (fr) that lies next to the alveoli
(al) to the side of the quadrulus. The cytopharyngeal ribbons
(cp mt) coming out of the filamentous reticulum have a spacing
that seems to be determined by the lattice-like arrangement of this
reticulum. A microtubular ribbon arises against each electron-opaque
row of nodes of the reticulum. A cytostomal cord (cc) borders
the cytosolic ends of these ribbons along the entire length of the
left side of the cytopharynx. The ribbons curve sharply over the cord
and pass out into the endoplasm. Three types of vesicles are
transported along these ribbons, discoidal vesicles (disc),
large acidosomes (ac) and small 100nm carrier vesicles
(cav). They all move along the ribbons from the endoplasm
toward the cytopharynx and the cytostomal cord toward the origins of
the microtubules. Discoidal vesicles reach the cytopharyngeal membrane
under the cord where they fuse. Acidosomes are too large to pass under
the cord and the 100nm carrier vesicles appear to have an affinity for
the acidosomes and fuse with these large vesicles before reaching the
cytopharyngeal membrane. EM taken on 3/28/80 by R. Allen with Hitachi
HU11A TEM. Neg. 8,500X. Bar = 0.5µm.
|