|
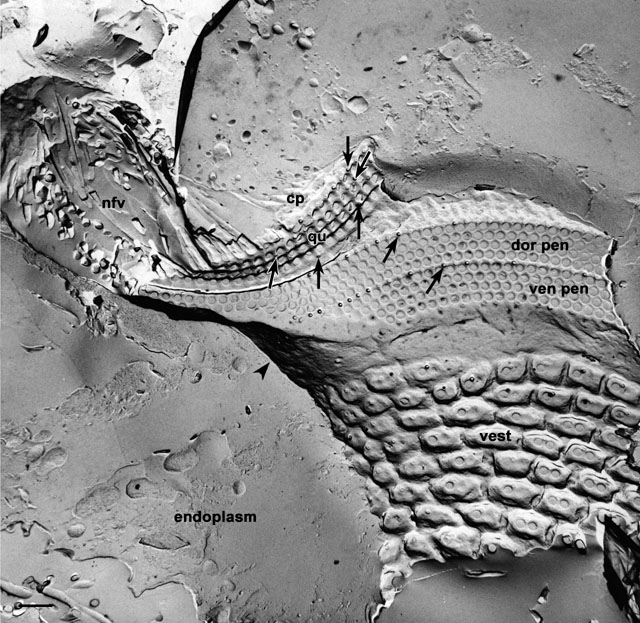
The oral region, illustrated here in a freeze-fracture image that
passed through its left side, opens at the mid-ventral part of the
cell. It consists of a funnel shaped vestibulum (vest) covered
with regular ciliature arising from normal somatic surface
depressions. The vestibulum opens into the tube-like buccal cavity
through an oral overture (see Fig. 22 of P. caudatum). On the
anterior dorsal surface and left side of the buccal cavity are the
three complex ciliary membranelles: the ventral peniculus (ven
pen), dorsal peniculus (dor pen) and quadrulus (qu).
Each membranelle is composed of four rows of closely packed
cilium/basal body complexes. Posterior to the vestibulum the floor of
the buccal cavity (arrowhead) is supported on the cytosolic
side by a filamentous reticulum which also covers the nonciliated
ribbed wall on the right side of the buccal cavity. The posterior
dorsal half of the buccal cavity opens through the cytostome (see Fig.
25 of P. caudatum and Fig 3 in this chapter) into the
cytopharynx (cp) and the developing food vacuole (nfv).
Since the structures of this oral complex in P.
multimicronucleatum are the same as those of P. caudatum,
it is suggested that reference be made to Figures 22-27 of P.
caudatum for an additional perspective. The micrographs of this
chapter of P. multimicronucleatum will focus on the structure
of the cytopharynx, the development of the food vacuole, the transport
of vesicles to the cytopharynx and postoral microtubular bundles.
arrows, rows of parasomal sacs. EM taken on 6/2/73 by D. Leaffer with
Hitachi HU11A TEM. Neg. 3,500X. Bar = 1µm. Published in J. Cell Biol.
63:904-922, 1974.
|